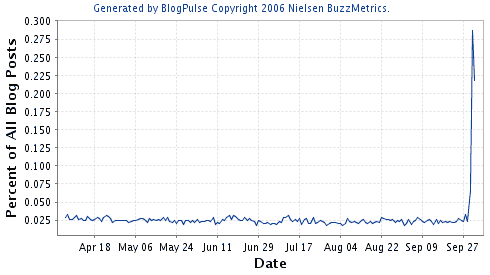
It’s been nearly forty-eight hours have passed since Radiohead’s surprise announcement set off an explosion of fandom around the web. Indeed, Blogpulse shows a more than 1300% increase in the number of posts mentioning the band from September 29 to October 1. Of course, a new Radiohead album is big news, especially after a four year wait, but the real source of conversation is the band’s decision to allow variable pricing of In Rainbows. Much of the commentary revolves around how this is a shot across the bow of the record labels.
In Rainbows is Radiohead’s first record since fulfilling their recording contract. That is to say that there was no record label involvement in the financing, production, marketing or distribution of the album. It’s yet another sign of the changing economics of the music industry in the digital era. Besides the usual “labels are dinosaurs” meme being bandied about, the aspect that strikes me the most about the In Rainbows announcement is the complete element of surprise.
It’s almost inconceivable that one of the world’s most watched band’s most anticipated albums could be sprung so suddenly on an unsuspecting populace.
Radiohead fans have known that there would be a new album “soon,” but a specific time frame was unknown. In fact, until as recently as week ago (Sept. 25) the Wikipedia page for the album maintained that it was to be released in 2008. There were no details other than suspected track titles and new songs played at live shows. We didn’t even know the album’s title until the other day. The fact that the band can say, “Hey it’s done and can be yours in a little more than a week,” that’s the real game changer here.
Consider the case with the band’s previous album, 2003’s Hail to the Thief. Whereas we’d heard nary a peep about In Rainbows, a surprisingly robust unmastered version of Hail to the Thief was leaked on the net TWO MONTHS before the official release date. Albums by other artists regularly appear on the net well ahead of their scheduled release date. Now, there’s the argument that leaked albums aren’t exactly a bad thing, but that’s not the point here.
The point is about control.
Now this is pure speculation, but it seems to me that without the involvement of record label personnel, Radiohead has been able to work in a more secured and isolated environment. Fewer spoons in the pot, so to speak, means fewer opportunities for unscrupulous individuals to make off with recorded materials. When there are so few people working closely on a project, I imagine that there’s much more loyalty and devotion as a whole and fewer people who feel that what they are doing is simply a job.
Added security and more artistic control? Chalk that up as another advantage to not working with a record label.
Of course, like Trent Reznor telling fans to steal his music, Radiohead can get away with this scheme because they’re a known quantity, having already benefitted from ten years of record label backing from a time when record labels were essential to lasting success. In 1997, there’s no way that OK Computer could have become one of the greatest albums ever released without the support of a major label. The media landscape of the late 90s was such that sufficient money to go big could only be found at a major corporation (EMI in Radiohead’s case).
Having generated all that cultural capital with the help of EMI’s resources and having a fan base that is already legion, there’s not much the band has to do at this point to stir up excitement. However, while they have generated the biggest buzz, Radiohead is not the first to distribute “donation-ware” music. Athens, Ga-based label Quote Unquote Records has been working in that fashion since 2006, billing itself at the first donation-based record label. And certainly there have been individual artists with Paypal buttons on their site, asking for contributions in exchange for free downloads. Though, it’s hard to find evidence on how financially successful that approach has been for the relatively obscure.
With a big name artist popularizing the idea, direct-to-consumer sales and personal value pricing are just more cracks in the business model of the record industry.
Historically, labels served the artists by putting money down to help promote, produce and distribute physical media. Throughout the 20th century, it was very expensive to shoot a music video and get posters printed and pay for studio time and hire recording technicians. The mass-production of thousands or millions of vinyl, cassettes or compact discs didn’t come cheap either. It’s impossible to have a record go platinum without manufacturing at least one million copies of it. The upfront money to do that was essentially on loan in the hopes that public interest in the artist would recoup costs and generate a healthy profit.
But since the boom of the MP3 and the increasing affordability and sophistication of “pro-am” music production, that system has been changing. Compared to even ten years ago, it’s exponentially cheaper to record, promote and distribute music using desktop computers and the Internet. Programs like Apple’s GarageBand make it relatively simple for actual garage bands or bedroom auteurs to create compelling, professional sounding music.
Add YouTube and music blogs (such as tunequest) to the mix and artists have a lot promotional muscle at their disposal. Top it off with low-cost DIY and pay-what-you-want digital distribution and the question becomes, “Who needs labels?”



 , for instant gratification.
, for instant gratification.